This past summer, the World Bank officially upgraded Cambodia to a "lower‑middle‑income country", a move that confirms the country's upwards economic trajectory over the past 20 years.
But despite this new status, which Cambodia shares with 51 other economies, including India, Vietnam and the Philippines, the country is still mostly associated with darker images: landmines, civil war and the Khmer Rouge regime. At best, perhaps, it’s seen as a new frontier destination for investment and tourism.
For development economists, though, this reclassification comes as no surprise: Cambodia’s economic development has earned it the title "olympian of growth" in some quarters, thanks to sustained double-digit growth between the years 1998 and 2015 (with the exception of 2009 and 2010, following the international financial crisis).
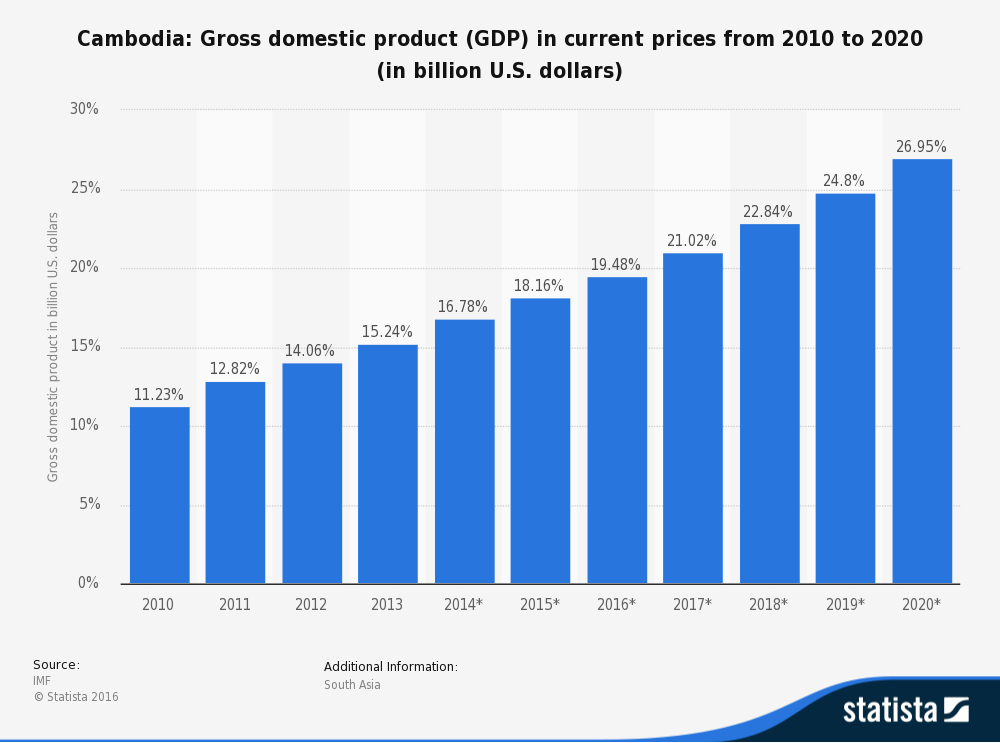
This rise is impressive not only for its rate but also for its resilience. The country has been growing at a stable rate over time, making it the world's sixth-fastest‑growing economy. While some would argue that "it started at a low level, so it's normal", the uniqueness of Cambodia's growth lies in its continuity over 20 years. Since 1950, only 13 economies in the world have grown at a rate above 7% per year for a quarter of a century or longer, and Cambodia is not an oil‑producing country. Its growth has been mostly driven by trade and by a buoyant demand for labour‑intensive manufactures (textiles and clothing), a booming tourism industry, growth in construction and, to a lesser extent, an increase in agricultural exports. New opportunities within the South-East Asian region have also emerged, fuelled by deeper integration in the ASEAN economic bloc.
GDP per capita has increased, inflation has been kept lower than 5% and the poverty rate has declined from 53% in 2004 to 16% in 2013. Yet there’s a long way to go before Cambodia achieves its vision of becoming an upper‑middle‑income nation and meeting all the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals by 2030 and turning into a developed country by 2050.
This blog was co-authored by H.E. Mr Pan Sorasak, Minister for Commerce, Cambodia and Mr Ratnakar Adhikari, Executive Director of the Executive Secretariat for the Enhanced Integrated Framework, and originally published on Monday 24 October 2016 in the World Economic Forum Agenda available at https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2016/10/can-trade-take-cambodia-from-dar…
If you would like to reuse any material published here, please let us know by sending an email to EIF Communications: eifcommunications@wto.org.


